State of water environmental issues
General Description of the Country
The Union of Myanmar is situated in South East Asia and the length of 2200 km is extending from the North to the South and 950 km from the East to the West. Myanmar has common borders with five neighboring countries and has a very long coastal line of about 2234 km along the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman sea.
Myanmar is one of the ASEAN member countries and endowed with rich natural resources cultivable land, available water resources and favorable climate. Myanmar is a forest - clad mountainous country, with plateaus, valleys and plains.
The total land area of Myanmar is about 261200 sq mile (67.65 million hectares ) and current land use in 2003-2004 status stood as follows:-
| Sr |
Type of land |
Land use
(million hectares) |
% |
Remarks |
| 1 |
Net sown area of crop land |
10.12 |
17.25
(Total cultivable land) |
14.96 |
25.5% of cultivable land |
| 2 |
Current fallow |
0.56 |
0.83 |
| 3 |
Cultivable waste |
6.57 |
9.71 |
| 4 |
Reserved forests |
14.99 |
22.15 |
|
| 5 |
Other forests |
18.49 |
27.34 |
|
| 6 |
Unclassified land not suitablefor crop land |
16.92 |
25.01 |
|
| Total |
67.65 |
100.00 |
|
The population of Myanmar according to statistical data of 2003-2004 is 52 million and the annual growth rate is about 2 percent.
|
Water resources and status of utilization
|
|
Myanmar is a country endowed with abundant water resources. The catchment area of Myanmar's ten principal river basins comprises about 737800 km². Potential water resources volume is about 1082 km³ for surface water and 495 cubic km for groundwater.as well constitute national water resources annually.
As an agro-base country of Myanmar, water utilization for agricultural sector stands for 90% while industry and domestic use is only about 10% of the total water use. The total utilization of the nation's water resources is only about 5 percent of the potential. It is clear that the physical potential for further development of water resources in Myanmar is quite substantial.
However with the increase of population and enhanced need for water for economic activities, there is increasing pressure on use of surface water and extraction of groundwater. Control and management of surface water and groundwater is therefore important for sustainable development of the country in future.
|
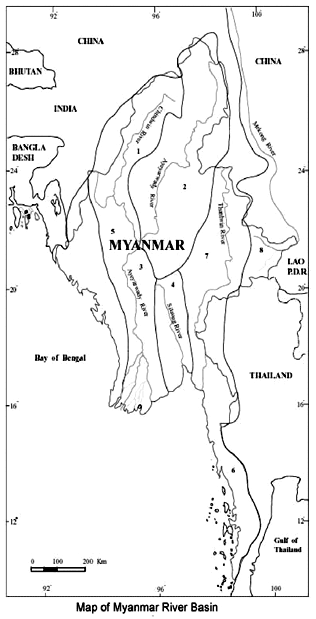 |
| Potential Water Resources in Myanmar |
| Sr |
River basin |
Catchment Area (km²) |
Inflow (km³) |
| 1 |
Chiundwin |
115300 |
141.29 |
| 2 |
Ayeyarwady (Upper) |
193300 |
227.92 |
| 3 |
Ayeyarwady(lower) |
95600 |
85.80 |
| 4 |
Sittoung |
34400 |
41.95 |
| 5 |
Rivers in Rakhaing State |
58300 |
139.25 |
| 6 |
River in Thanintharyi Division |
40600 |
130.93 |
| 7 |
Thanlwin ( in Myanmar) |
158000 |
257.92 |
| 8 |
Mekong (in Myanmar) |
28600 |
17.63 |
| 9 |
Bilin River and other rivulets |
8400 |
31.17 |
| 10 |
Bago River |
5300 |
8.02 |
| Total |
737800 |
1081.88 |
|
| Potential Groundwater in Myanmar |
| Sr |
River basin |
Catchment Area (km²) |
Inflow(km³) |
| 1 |
Chiundwin |
115300 |
57.58 |
| 2 |
Ayeyarwady (Upper) |
193300 |
92.60 |
| 3 |
Ayeyarwady(lower) |
95600 |
153.25 |
| 4 |
Sittoung |
48100 |
28.40 |
| 5 |
Rivers in Rakhaing State |
58300 |
41.77 |
| 6 |
River in Thanintharyi Division |
40600 |
39.28 |
| 7 |
Thanlwin ( in Myanmar) |
158000 |
74.78 |
| 8 |
Mekong (in Myanmar) |
28600 |
7.05 |
| Total |
737800 |
494.71 |
|
The present status of water environment
The percentage of people cover by safe drinking water and sanitation facilities are still very low in the country compared to the global status. In Myanmar rural water supply activities were started in 1952 to provide safe drinking water and implement environmental sanitation works for the rural populace. At present, with the assistance of international organizations, several water supply and sanitation projects are being implemented. Up to the end of August 1995 Government implemented, various rural water supply activities covering for 12.5 million of the population.
Most of the irrigation reservoirs were sited on the tributaries and streamlets of main water resources. Consequently while not impeding or hindering the flow of main water resources, the impact of the dams on environment have also been negligible. Similarly no major reservoirs that could impede flow have been constructed in the catchment of the Ayeyarwady river, which is Myanmar's main water channel.
Consumption of storage water from reservoir is not only for the irrigation but also for drinking purpose. Analysis of water quality from most of reservoirs is carried out, and most of the results show water quality of storage reservoir is suitable for agriculture purpose. The results of the some of the reservoirs are followings.
Analytical Data for Water
| (1) Sedawgyi Dam |
| Date Sampled = 5.6.2003 |
| Sr |
Ions |
Symbol |
Units |
Results |
| 1 |
Calcium |
Ca++ |
me/L |
0.64 |
| 2 |
Magnesium |
Mg++ |
" |
0.72 |
| 3 |
Sodium |
Na+ |
" |
0.37 |
| 4 |
Potassium |
K+ |
" |
– |
| 5 |
Carbonate |
CO3= |
" |
N.D |
| 6 |
Bicarbonate |
HCO3– |
" |
0.08 |
| 7 |
Sulphate |
SO4= |
" |
2.16 |
| 8 |
Chloride |
CL– |
" |
0.38 |
| 9 |
Iron |
Fe++ |
mg/L |
N.D |
| 10 |
Total Dissolved solids |
TDS |
ppm |
110.72 |
| 11 |
Soluble sodium percentage |
SSP |
% |
21.39 |
| 12 |
Sodium adsorption ratio |
SAR |
– |
0.45 |
| 13 |
Residual sodium carbonate |
RSC |
me/L |
-1.28 |
| 14 |
pH |
pH |
– |
6.46 |
| 15 |
Electrical conductivity |
E.C |
µmhos/cm |
173 |
| 16 |
Classification |
|
– |
C1S1 |
|
| N.D = Not detected |
| (2) Ngamoeyeik Dam |
| Date Sampled = 17.5.2003 |
| Sr |
Ions |
Symbol |
Units |
Results |
| 1 |
Calcium |
Ca++ |
me/L |
0.32 |
| 2 |
Magnesium |
Mg++ |
" |
0.68 |
| 3 |
Sodium |
Na+ |
" |
0.01 |
| 4 |
Potassium |
K+ |
" |
– |
| 5 |
Carbonate |
CO3= |
" |
N.D |
| 6 |
Bicarbonate |
HCO3– |
" |
0.10 |
| 7 |
Sulphate |
SO4= |
" |
1.56 |
| 8 |
Chloride |
CL– |
" |
0.14 |
| 9 |
Iron |
Fe++ |
mg/L |
N.D |
| 10 |
Total Dissolved solids |
TDS |
ppm |
64.64 |
| 11 |
Soluble sodium percentage |
SSP |
% |
0.99 |
| 12 |
Sodium adsorption ratio |
SAR |
– |
0.01 |
| 13 |
Residual sodium carbonate |
RSC |
me/L |
-0.90 |
| 14 |
pH |
pH |
– |
7.20 |
| 15 |
Electrical conductivity |
E.C |
µmhos/cm |
101 |
| 16 |
Classification |
|
– |
C1S1 |
|
| N.D = Not detected |
| (3) Sun Chaung Dam |
| Date Sampled = 15.4.2003 |
| Sr |
Ions |
Symbol |
Units |
Results |
| 1 |
Calcium |
Ca++ |
me/L |
1.20 |
| 2 |
Magnesium |
Mg++ |
" |
2.24 |
| 3 |
Sodium |
Na+ |
" |
1.36 |
| 4 |
Potassium |
K+ |
" |
- |
| 5 |
Carbonate |
CO3= |
" |
0.08 |
| 6 |
Bicarbonate |
HCO3– |
" |
0.16 |
| 7 |
Sulphate |
SO4= |
" |
1.76 |
| 8 |
Chloride |
CL– |
" |
0.28 |
| 9 |
Iron |
Fe++ |
mg/L |
N.D |
| 10 |
Total Dissolved solids |
TDS |
ppm |
307.20 |
| 11 |
Soluble sodium percentage |
SSP |
% |
28.33 |
| 12 |
Sodium adsorption ratio |
SAR |
– |
1.04 |
| 13 |
Residual sodium carbonate |
RSC |
me/L |
-3.20 |
| 14 |
pH |
pH |
– |
6.70 |
| 15 |
Electrical conductivity |
E.C |
µmhos/cm |
480 |
| 16 |
Classification |
|
– |
C2S1 |
|
| N.D = Not detected |
| (4) Ketlan Dam (Natogyi Township) |
| Sr |
Ions |
Units |
Results |
| 15.6.01 |
15.9.01 |
20.3.02 |
24.10.02 |
12.9.03 |
30.10.03 |
| 1 |
Calcium |
me/L |
1.53 |
1.40 |
1.85 |
8.34 |
0.02 |
1.87 |
| 2 |
Magnesium |
" |
6.15 |
11.78 |
8.06 |
9.76 |
7.79 |
4.09 |
| 3 |
Sodium |
" |
26.90 |
25.0 |
26.26 |
70.93 |
29.89 |
7.88 |
| 4 |
Potassium |
" |
0.12 |
0.34 |
0.09 |
0.09 |
0.24 |
0.12 |
| 5 |
Carbonate |
" |
2.01 |
2.39 |
0.32 |
6.32 |
1.39 |
Nil |
| 6 |
Bicarbonate |
" |
6.03 |
4.94 |
6.92 |
0.20 |
6.32 |
4.06 |
| 7 |
Sulphate |
" |
18.56 |
20.87 |
70.85 |
19.01 |
24.31 |
6.76 |
| 8 |
Chloride |
" |
8.69 |
8.16 |
9.18 |
6.63 |
7.66 |
3.19 |
| 9 |
Iron |
mg/L |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| 10 |
Total Dissolved solids |
ppm |
3192 |
3291 |
4316 |
2791.68 |
3847.68 |
1629 |
| 11 |
Soluble sodium percentage |
% |
77.52 |
64.90 |
72.50 |
49.64 |
78.78 |
56.45 |
| 12 |
Sodium adsorption ratio |
– |
27.45 |
90.48 |
32.35 |
11.92 |
30.50 |
11.54 |
| 13 |
Residual sodium carbonate |
me/L |
0.36 |
0 |
-2.67 |
-11.58 |
-0.1 |
-1.90 |
| 14 |
pH |
– |
8.98 |
8.98 |
8.63 |
7.62 |
8.77 |
8.67 |
| 15 |
Electrical conductivity |
µmhos/cm |
4988 |
5143 |
6744 |
4362 |
6012 |
2545 |
| 16 |
Classification |
– |
C4S4 |
C4S4 |
C4S4 |
C4S3 |
C4S4 |
C4S4 |
|
| (5) Kyauktalone Dam (Taungtha Township) |
| Sr |
Ions |
Symbol |
Units |
Results |
| 20.3.03 |
23.7.03 |
17.11.03 |
| 1 |
Calcium |
Ca++ |
me/L |
1.01 |
1.12 |
0.80 |
| 2 |
Magnesium |
Mg++ |
" |
1.01 |
1.88 |
0.56 |
| 3 |
Sodium |
Na+ |
" |
7.49 |
3.65 |
7.04 |
| 4 |
Potassium |
K+ |
" |
- |
- |
- |
| 5 |
Carbonate |
CO3= |
" |
0.90 |
0.08 |
0.80 |
| 6 |
Bicarbonate |
HCO3– |
" |
4.30 |
0.12 |
3.20 |
| 7 |
Sulphate |
SO4= |
" |
7.95 |
2.20 |
7.92 |
| 8 |
Chloride |
CL– |
" |
3.12 |
0.88 |
2.27 |
| 9 |
Iron |
Fe++ |
mg/L |
N.D |
N.D |
N.D |
| 10 |
Total Dissolved solids |
TDS |
ppm |
579.20 |
408 |
537.60 |
| 11 |
Soluble sodium percentage |
SSP |
% |
82.76 |
54.89 |
83.81 |
| 12 |
Sodium adsorption ratio |
SAR |
– |
7.45 |
2.98 |
8.59 |
| 13 |
Residual sodium carbonate |
RSC |
me/L |
3.18 |
-2.80 |
2.64 |
| 14 |
pH |
pH |
– |
8.2 |
6.8 |
7.7 |
| 15 |
Electrical conductivity |
E.C |
µmhos/cm |
905 |
665 |
840 |
| 16 |
Classification |
|
– |
C3S2 |
C2S1 |
C3S2 |
|
| N.D = Not detected |
Formation of saline soil in the irrigated tract due to drainage and water logging problems are found in some localized area in central Myanmar.
There is also sedimentation problem in some major river systems in Myanmar. As a result of depletion of forest in the watershed areas and as a counter measure, Irrigation Department has being participated actively and cooperated with Forest Department for reforestation activities in some watershed area.
|

